MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Information
Disclaimer: THIS WEBSITE DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only.
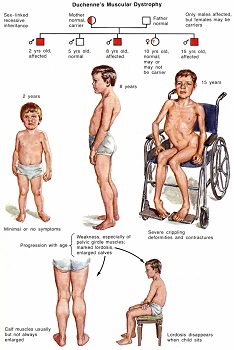
Muscular Dystrophy is a serious medical condition in which somebody’s muscles gradually become weaker from the time they are born .
Cause:
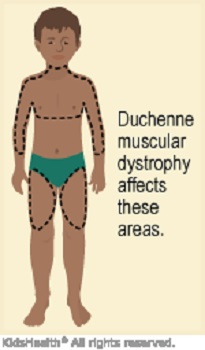
Muscular dystrophy (MD) refers to a group of more than 30 genetic diseases that cause progressive weakness and degeneration of skeletal muscles used during voluntary movement.These disorders vary in age of onset, severity and pattern of affected muscles. Certain genes are involved in making proteins that protect muscle fibers. Muscular dystrophy occurs when one of these genes is defective. Each form of muscular dystrophy is caused by a genetic mutation particular to that type of the disease. Most of these mutations are inherited.Damaged muscles become progressively weaker. Most people who have the condition eventually need a wheelchair.
Symptoms begin in childhood, mostly it affects the male kids.Other types don’t surface until adulthood. Duchenne type muscular dystrophy, is the most common form. It occurs in both sexes and in all ages and races.
Common Symptoms
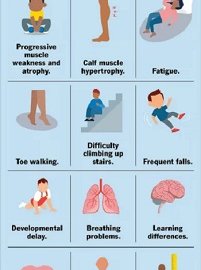
- Frequent falls
- Difficulty rising from a lying or sitting position
- Trouble running and jumping
- Waddling gait
- Walking on the toes
- Large calf muscles
- Muscle pain and stiffness
- Delayed growth
When to see a doctor
Seek medical advice if you notice signs of muscle weakness — such as increased clumsiness and falling — in you or your child. There’s no cure for muscular dystrophy. However aids or surgery can help manage symptoms, may help maintain function, slow the course of the disease but lifespan is often shortened.
Keep in mind that not every patient will respond to these muscular dystrophy treatments in the same way.Monitoring symptom progress,individual reactions and warning signs of complications is important.Ultimately every patient will need to determine their own best treatment approach with their team of professional health care providers.Early intervention can also be very beneficial for reducing worsened symptoms.
Diagnosis
Your doctor is likely to start with a medical history and physical examination.
After that, your doctor might recommend:
- Enzyme tests. Damaged muscles release enzymes, such as creatine kinase (CK), into your blood. high blood levels of CK suggest a muscle disease.
- Genetic testing. Blood samples can be examined for mutations in some of the genes that cause types of muscular dystrophy.
- Muscle biopsy. A small piece of muscle can be removed through an incision or with a hollow needle. Analysis of the tissue sample can distinguish muscular dystrophies from other muscle diseases.
- Heart-monitoring tests (electrocardiography and echocardiogram). These tests are used to check heart function.
- Lung-monitoring tests. These tests are used to check lung function.
- Electromyography. An electrode needle is inserted into the muscle to be tested. Electrical activity is measured as you relax and as you gently tighten the muscle. Changes in the pattern of electrical activity can confirm a muscle disease.

Coping and Support
A diagnosis of muscular dystrophy can be extremely challenging.To help you cope, find someone to talk with. You might feel comfortable discussing your feelings with a friend or family member, or you might prefer meeting with a formal support group or health care professionals. Ask your doctor
about ways to discuss this progressive condition with your child, don’t bottle up your feelings, concerns and frustrations. This will negatively affect the well-being of you and your family.
https://musculardystrophynews.com/columns/gift-ideas-disabilities/
Sarthak smiling pics with family members, coping with MD with a positive attitude.